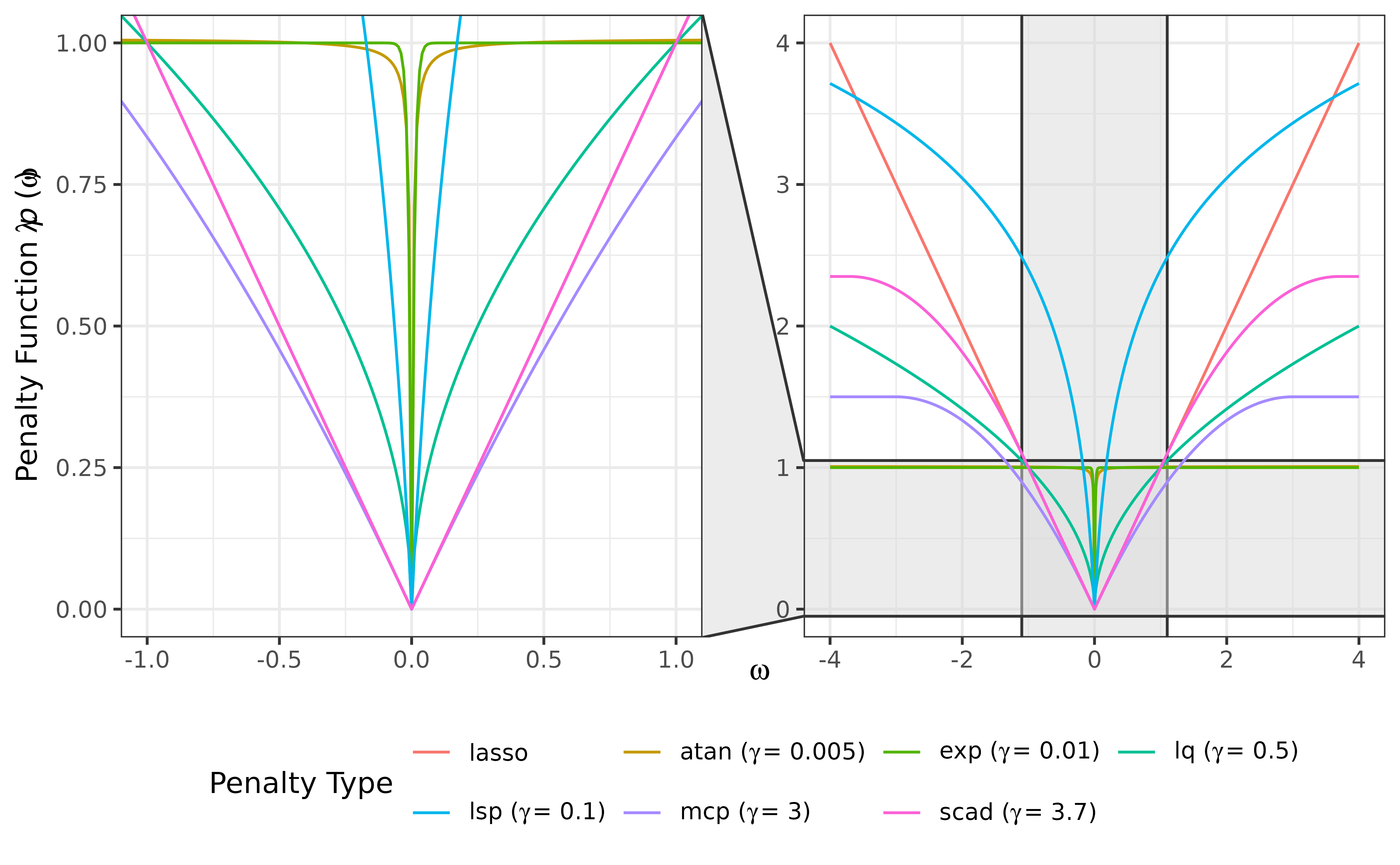
Compute one or more penalty values for a given omega, allowing
vectorized specifications of penalty, lambda, and gamma.
Arguments
- omega
A numeric value or vector at which the penalty is evaluated.
- penalty
A character string or vector specifying one or more penalty types. Available options include:
"lasso": Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Tibshirani 1996; Friedman et al. 2008) .
"atan": Arctangent type penalty (Wang and Zhu 2016) .
"exp": Exponential type penalty (Wang et al. 2018) .
"lq": Lq penalty (Frank and Friedman 1993; Fu 1998; Fan and Li 2001) .
"lsp": Log-sum penalty (Candès et al. 2008) .
"mcp": Minimax concave penalty (Zhang 2010) .
"scad": Smoothly clipped absolute deviation (Fan and Li 2001; Fan et al. 2009) .
If
penaltyhas length 1, it is recycled to the common length determined bypenalty,lambda, andgamma.- lambda
A non-negative numeric value or vector specifying the regularization parameter. If
lambdahas length 1, it is recycled to the common length determined bypenalty,lambda, andgamma.- gamma
A numeric value or vector specifying the additional parameter for the penalty function. If
lambdahas length 1, it is recycled to the common length determined bypenalty,lambda, andgamma. The penalty-specific defaults are:"atan": 0.005
"exp": 0.01
"lq": 0.5
"lsp": 0.1
"mcp": 3
"scad": 3.7
For
"lasso",gammais ignored.
Value
A data frame with S3 class "penalty" containing:
- omega
The input
omegavalues.- penalty
The penalty type for each row.
- lambda
The regularization parameter used.
- gamma
The additional penalty parameter used.
- value
The computed penalty value.
The number of rows equals
max(length(penalty), length(lambda), length(gamma)).
Any of penalty, lambda, or gamma with length 1
is recycled to this common length.
References
Candès EJ, Wakin MB, Boyd SP (2008).
“Enhancing Sparsity by Reweighted \(\ell_1\) Minimization.”
Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 14(5), 877–905.
doi:10.1007/s00041-008-9045-x
.
Fan J, Feng Y, Wu Y (2009).
“Network Exploration via the Adaptive LASSO and SCAD Penalties.”
The Annals of Applied Statistics, 3(2), 521–541.
doi:10.1214/08-aoas215
.
Fan J, Li R (2001).
“Variable Selection via Nonconcave Penalized Likelihood and its Oracle Properties.”
Journal of the American Statistical Association, 96(456), 1348–1360.
doi:10.1198/016214501753382273
.
Frank LE, Friedman JH (1993).
“A Statistical View of Some Chemometrics Regression Tools.”
Technometrics, 35(2), 109–135.
doi:10.1080/00401706.1993.10485033
.
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2008).
“Sparse Inverse Covariance Estimation with the Graphical Lasso.”
Biostatistics, 9(3), 432–441.
doi:10.1093/biostatistics/kxm045
.
Fu WJ (1998).
“Penalized Regressions: The Bridge versus the Lasso.”
Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 7(3), 397–416.
doi:10.1080/10618600.1998.10474784
.
Tibshirani R (1996).
“Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso.”
Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 58(1), 267–288.
doi:10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x
.
Wang Y, Fan Q, Zhu L (2018).
“Variable Selection and Estimation using a Continuous Approximation to the \(L_0\) Penalty.”
Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 70(1), 191–214.
doi:10.1007/s10463-016-0588-3
.
Wang Y, Zhu L (2016).
“Variable Selection and Parameter Estimation with the Atan Regularization Method.”
Journal of Probability and Statistics, 2016, 6495417.
doi:10.1155/2016/6495417
.
Zhang C (2010).
“Nearly Unbiased Variable Selection under Minimax Concave Penalty.”
The Annals of Statistics, 38(2), 894–942.
doi:10.1214/09-AOS729
.